The Modigliani-Miller theorem forms the basis for modern thinking on capital structure. The basic theorem states that, in the absence of taxes, bankruptcy costs, and asymmetric information, and in an efficient market, the value of a firm is unaffected by how that firm is financed. It does not matter if the firm’s capital is raised by issuing stock or selling debt. It does not matter what the firm’s dividend policy is. Therefore, the Modigliani-Miller theorem is also often called the capital structure irrelevance principle.
The theorem was originally proven under the assumption of no taxes. It is made up of two propositions which can also be extended to a situation with taxes.
Consider two firms which are identical except for their financial structures. The first (Firm U) is unlevered: that is, it is financed by equity only. The other (Firm L) is levered: it is financed partly by equity, and partly by debt. The Modigliani-Miller theorem states that the value of the two firms is the same.
Without taxes
Proposition I: 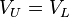 where VU is the value of an unlevered firm = price of buying a firm composed only of equity, and VL is the value of a levered firm = price of buying a firm that is composed of some mix of debt and equity.
where VU is the value of an unlevered firm = price of buying a firm composed only of equity, and VL is the value of a levered firm = price of buying a firm that is composed of some mix of debt and equity.
To see why this should be true, suppose an investor is considering buying one of the two firms U or L. Instead of purchasing the shares of the levered firm L, he could purchase the shares of firm U and borrow the same amount of money B that firm L does. The eventual returns to either of these investments would be the same. Therefore the price of L must be the same as the price of U minus the money borrowed B, which is the value of L’s debt.
This discussion also clarifies the role of some of the theorem’s assumptions. We have implicitly assumed that the investor’s cost of borrowing money is the same as that of the firm, which need not be true in the presence of asymmetric information or in the absence of efficient markets.
Proposition II:


- ke is the required rate of return on equity, or cost of equity.
- k0 is the cost of capital for an all equity firm.
- kd is the required rate of return on borrowings, or cost of debt.
- D / E is the debt-to-equity ratio.
This proposition states that the cost of equity is a linear function of the firm’s debt to equity ratio. A higher debt-to-equity ratio leads to a higher required return on equity, because of the higher risk involved for equity-holders in a company with debt. The formula is derived from the theory of weighted average cost of capital.
These propositions are true assuming the following assumptions:
- no taxes exist,
- no transaction costs exist, and
- individuals and corporations borrow at the same rates.
These results might seem irrelevant (after all, none of the conditions are met in the real world), but the theorem is still taught and studied because it tells us something very important. That is, capital structure matters precisely because one or more of these assumptions are violated. It tells us where to look for determinants of optimal capital structure and how those factors might affect optimal capital structure.
With taxes
Proposition I:
where
- VL is the value of a levered firm.
- VU is the value of an unlevered firm.
- TCD is the tax rate (TC) x the value of debt (D)
This means that there are advantages for firms to be levered, since corporations can deduct interest payments. Therefore leverage lowers tax payments. Dividend payments are non-deductible.
Proposition II:
where
- rE is the required rate of return on equity, or cost of equity.
- r0 is the cost of capital for an all equity firm.
- rD is the required rate of return on borrowings, or cost of debt.
- D / E is the debt-to-equity ratio.
- Tc is the tax rate.
The same relationship as earlier described stating that the cost of equity rises with leverage, because the risk to equity rises, still holds. The formula however has implications for the difference with the WACC. Their second attempt on capital structure included taxes and identified that as the level of gearing increases by replacing equity with cheap debt the level of the WACC drops and an optimal capital structure does indeed exist at a point where debt is 100%
The following assumptions are made in the propositions with taxes:
- corporations are taxed at the rate TC on earnings after interest,
- no transaction costs exist, and
- individuals and corporations borrow at the same rate
Miller and Modigliani published a number of follow-up papers discussing some of these issues.
The theorem was first proposed by F. Modigliani and M. Miller in 1958.

