What is a Yield?
Yield is the interest paid by the bond expressed as a % of its current market price. E.g. the yield of 7.99% 2017 G Sec at market price of INR 100 will be 7.99%, at INR 90 will be 8.87% and at INR 110 will be 7.26%.
What is a Yield Curve?
Yield Curve is the graphical description of the relationship between yields on bonds of same credit quality but with different maturities. By having a look at the yield curve one can see what rates are being offered by bonds of the same credit quality of different maturities. There are 3 different types of yield curve shapes: 1) Normal or positively sloping yield curve. 2) Inverted yield curve. 3) Flat yield curve.
Inverted Yield Curve
Flat Yield Curve
Type of Yield Curve
The shape of the yield curve is closely scrutinized because it helps to give an idea of future interest rate change and economic activity. Due to this historical correlation, the yield curve is often seen as an forecast of the turning points of the business cycle.
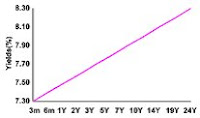
Normal Yield Curve
A normal yield curve is yield curve in which short-term debt instruments have a lower yield than long-term debt instruments of the same credit quality. This gives the yield curve an upward slope. This curve is also referred to as positive yield curve. This yield curve is considered normal because the market usually expects more compensation for greater risk. Longer-term bonds are exposed to more risks such as changes in interest rates and an increased exposure to potential defaults. Also, investing money for a long period of time means an investor is unable to use the money in other ways, so the investor is compensated for this through the time value of money component of the yield.
Inverted Yield Curve
An inverted yield curve occurs in an interest rate environment in which long-term debt instruments have a lower yield than short-term debt instruments of the same credit quality. This type of yield curve is the rarest of the three main curve types and is considered to be a predictor of economic recession. Partial inversion occurs when only some of the short-term Treasuries (One or five years) have higher yields than the Thirty year Treasuries do. An inverted yield curve is sometimes referred to as a negative yield curve. Historically, inversions of the yield curve have preceded many of the US recessions.
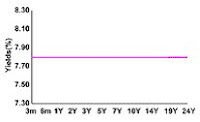
Flat Yield Curve
A flat yield curve is a yield curve in which there is little difference between short-term and long-term rates for bonds of the same credit quality. This type of yield curve is often seen during transitions between normal and inverted curves. When short- and long-term bonds are offering equivalent yields, there is usually little benefit in holding the longer-term instruments – that is, the investor does not gain any excess compensation for the risks associated with holding longer-term securities.